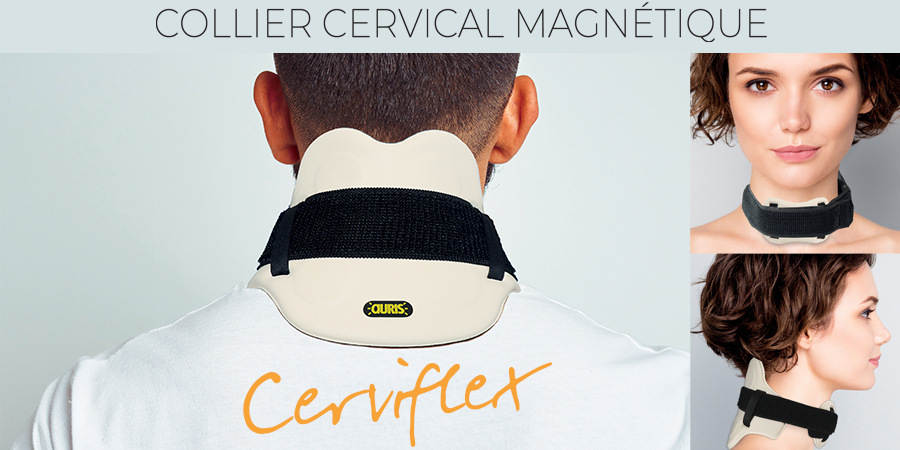
New Auris cervical collar: the Cerviflex
You have been suffering from neck pain since a trauma or for a long time without any apparent reason. Cervicalgia, which literally means "neck pain", does not refer to a specific pathology but to a symptom that may correspond to several problems. Nowadays, many people complain of neck pain. It can take different forms: acute, chronic, sudden onset or gradual... In most cases, it's a benign problem, but its impact on daily life is no less significant, especially if it becomes chronic.
After months of research, prototypes and tests, Auris has developed its new magnetic cervical collar: the Cerviflex.
New material, new design, new shape - everything is new. Enveloping, flexible and resistant, it follows every movement of the neck, without discomfort or resistance, and adapts to every morphology.
Its "high comfort" cushion prevents unpleasant pressure on the glottis. Developed in conjunction with health professionals, Cerviflex is the natural and effective answer to neck pain. Its 4 powerful neodymium magnets provide fast, lasting relief thanks to their residual effect.
Discover the new magnetic cervical collar: Cerviflex, a 100% Auris creation.
The extraordinary health benefits of olives
The olive, that delicious, fragrant little fruit of which there are almost 500 different varieties, is bursting with nutrients that are good for your health. Incorporating olives into your daily diet (without overdoing it) can boost your body from head to toe.
Olives are particularly rich in vitamin E, a powerful antioxidant that protects the body, and vitamin K1, which helps blood to clot properly. This fruit is also appreciated for its high selenium and iron content, which boosts the immune system.
At 162 kcal per 100 g, olives are one of the lowest-calorie savoury snacks (145 calories for green olives; 170 kcal for black olives). So they're a good choice for an aperitif.
But beware: olives are very salty (100g of olives is equivalent to 81% of the recommended daily intake).
Eating olives regularly helps to fight inflammation, as they contain polyphenols. This compound is known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antifungal and antimicrobial properties.
They are therefore capable of :
- Reduce oxidative stress in brain cells, improve memory, maintain healthy eyes and fight wrinkles.
- combat macular degeneration, cataracts and glaucoma.
- boost good cholesterol in the blood and promote better insulin sensitivity, as well as reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease and hypertension.
- stimulate the activity of the gall bladder and liver, helping the ball to pass through the intestine.
Olive oil can also be used in cosmetics for its moisturising, anti-ageing and anti-bacterial properties. It can be used as a make-up remover (with rinsing) or as a moisturiser after a shower.
Be careful, however, to use it sparingly, as it is very oily. And of course, choose organic olive oil.

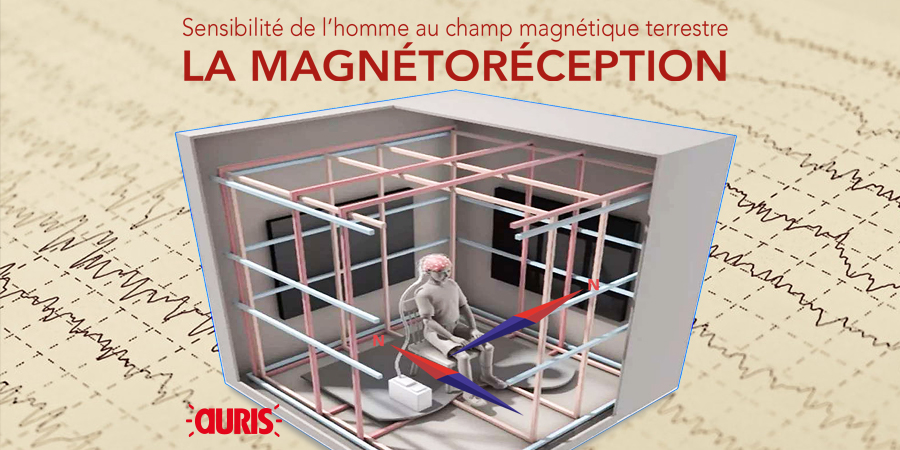
New study: humans do feel the Earth's magnetic field
The Earth's magnetic field, although weak, is perceived by a variety of animals. Many vertebrates respond to magnetic stimuli: fish, amphibians, reptiles and birds. Mammals include whales, rodents, bats, cows and dogs. In the microbial world too, bacteria have magnetite crystals, a kind of compass, which help to orientate the cell's swimming motion according to the lines of the magnetic field. Magnetite is present in many animals, including the human brain.
Researchers in California have carried out experiments to demonstrate magnetoreception in humans: our brains unconsciously detect the Earth's magnetic field. Researchers at the Caltech Institute of Technology (California) wanted to capture these unconscious reactions of the brain. They created a Faraday cage (isolated from the Earth's magnetic field) in which a static magnetic field of 35 µT (microTesla) could be applied and directed in different directions. They monitored the electrical activity of the brains of the 34 participants using electroencephalograms.
During the experiment, each participant had to remain seated on a chair in this isolated chamber for 7 minutes, eyes closed, while the magnetic field was modified.
The field could rotate clockwise or anti-clockwise, as if you were moving your head to the left or right, and it was oriented downwards at an angle of 60° to the horizontal, like the local terrestrial magnetic field.
The participants felt nothing in particular when the magnetic field was modified, but their brains seemed to react. The researchers observed that the amplitude of the participants' alpha waves decreased significantly. Alpha waves (frequency of 10 Hz) dominate an electroencephalogram when we are relaxed. When a stimulus suddenly appears, the rhythm of the alpha waves is desynchronised and their amplitude drops. This phenomenon, known as "alpha event-related desynchronisation" or alpha-ERD, can occur, for example, when the brain perceives a flash of light. The alpha-ERD means that the brain has picked up a stimulus and is processing the information.
The study shows that the human brain reacts to variations in the Earth's magnetic field. According to Caltech, "we have a sensory system that processes the geomagnetic field all around us".
So a new question arises: what could be the purpose of this geomagnetic sense in humans? Perhaps our hunter-gatherer ancestors used it for orientation and survival.
In the experiment, there were differences between the participants: some hardly reacted at all, while others had a 50% drop in alpha waves after the magnetic change. This suggests that human beings vary in their geomagnetic sensitivity.
These results confirm those of the various clinical studies conducted by Auris, which show that there are hyper-rapid, fast and slow responders to magnetic therapy.
Solar storms could have an impact on our health
Solar storms occur frequently and can have an impact on our planet, particularly on electrical systems and transformers, but also on our health.The magnetic impact caused by this phenomenon is thought to interfere directly with the nervous and cardiac systems.
This, at any rate, is the conclusion of a study published by Boston researchers a few weeks ago in Science.
The researchers monitored 809 men aged 74 on average and repeatedly measured their cardiac activity.
During intense geomagnetic disturbances due to solar storms, the researchers obtained surprising results. They explain that they observed "an almost immediate effect". This is the first study to demonstrate the potential adverse effects of geomagnetic activity on heart rate.
A previous study had already shown that electromagnetic disturbances induced by solar activity increased the risk of mortality and cardiovascular problems.
Unfortunately for heart patients, the Sun has entered a new cycle, with peak activity expected in 2025. Solar storms are likely to become increasingly frequent in the months ahead.
So it's important to be informed in real time about the sun's activity, and when will we see a solar weather forecast?

At what age do you become right- or left-handed?
Manual laterality", the preference for using one hand rather than the other, seems to be determined even before birth, from life in utero. According to an Irish study, 90% of foetuses suck their right thumb more often and 10% their left thumb. Almost all 'right-handed' foetuses will be so in adulthood, while only two-thirds of left-handed babies will be 'true' left-handers...
However, in the first few months of life, all children have a fluctuating laterality: a French study carried out on 4-month-old babies showed a preference for the left hand when the child reaches for an object without grasping it, and a preference for the right hand when it wants to grasp an object.
Then, as the child grows up and routinely handles objects, his manual preference becomes more obvious, from the age of 2... Finally, it is around 6 to 7 years old that this laterality stabilises with the learning of writing, which requires very fine manual coordination and therefore leads to a definitive choice of hand.
In the end, 10% of adults are left-handed, compared with 90% who are right-handed, among whom are hidden... left-handed people.
They write and make gestures with their right hand and others with their left, but learning does not completely eliminate the spontaneous preference.
Putting a toy in the right hand of a left-handed baby will not make him or her "truly" right-handed.
British geneticists have shown that the LRRTM1 gene favours left-handedness. And family studies also point to a genetic transmission of laterality: right-handers have a 9% probability of having a left-handed child, whereas this probability rises to 30% for a left-handed couple.

